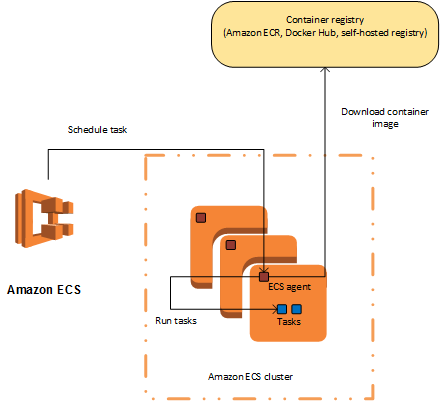
When using EC2 instance it has both Docker Engine and an ECS agent installed. Using either the ECS console or the AWS CLI, you can define, launch, and manage containers on that EC2 instance.
Here are some ECS concepts:
ECS CLI: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonECS/latest/developerguide/ECS_CLI.html
ECS Deploy tool: http://ufoships.com/quick-start/
ECS resources: https://github.com/nathanpeck/awesome-ecs#autoscaling
Four Steps to Run ECS Clusters on EC2 Spot Instances:
- Tasks: metadata defining an application and its network, storage, and security environment
- Services: software that launches, monitors, and controls your containers
- Containers: definitions for the machines that will run a task
ECS CLI: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonECS/latest/developerguide/ECS_CLI.html
ECS Deploy tool: http://ufoships.com/quick-start/
ECS resources: https://github.com/nathanpeck/awesome-ecs#autoscaling
Four Steps to Run ECS Clusters on EC2 Spot Instances:
https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/spot/containers-for-less/get-started/
ECS Draining: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonECS/latest/developerguide/container-instance-draining.html
Scheduling on ECS/EC2:
https://github.com/aws-samples/amazon-ecs-catsndogs-workshop/blob/master/Lab-1-Artifacts/lab1-detailed-steps.md
https://engineering.depop.com/ahead-of-time-scheduling-on-ecs-ec2-d4ef124b1d9e
https://garbe.io/blog/2017/04/12/a-better-solution-to-ecs-autoscaling/
https://segment.com/blog/when-aws-autoscale-doesn-t/
Spot Instance Drainer: https://medium.com/@kevintruckenmiller/aws-spot-instances-and-ecs-b61c5802b375
Metric Math: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/using-metric-math.html
Here is nice script to create whole environment. Can use Application Load Balancing with ECS:
Here is another script to manage ECS:
https://www.benedict.cloud/2019/02/10/full-lamp-docker-and-aws-introduction-tutorial/

ECS Draining: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonECS/latest/developerguide/container-instance-draining.html
Scheduling on ECS/EC2:
https://github.com/aws-samples/amazon-ecs-catsndogs-workshop/blob/master/Lab-1-Artifacts/lab1-detailed-steps.md
https://engineering.depop.com/ahead-of-time-scheduling-on-ecs-ec2-d4ef124b1d9e
https://garbe.io/blog/2017/04/12/a-better-solution-to-ecs-autoscaling/
https://segment.com/blog/when-aws-autoscale-doesn-t/
Spot Instance Drainer: https://medium.com/@kevintruckenmiller/aws-spot-instances-and-ecs-b61c5802b375
Metric Math: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/using-metric-math.html
ECS Fargate review:
Here is nice script to create whole environment. Can use Application Load Balancing with ECS:
echo "[*] [$( date +'%H:%M:%S')] Create Application Load Balancer in chosen subnets..."
alb_response=$( aws elbv2 --region ${region} create-load-balancer --name ${loadbalancer_name} --subnets ${subnet_id_1} ${subnet_id_2} --security-groups ${group_id} )
alb_arn=$( echo -e "${alb_response}" | jq '.LoadBalancers[] | .LoadBalancerArn' | tr -d '"' )
alb_dnsname=$( echo -e "${alb_response}" | jq '.LoadBalancers[] | .DNSName' | tr -d '"')
echo "[*] [$( date +'%H:%M:%S')] Create Target Group for ECS instances (targeting port ${target_port})..."
target_group_response=$( aws elbv2 --region ${region} create-target-group --name ${loadbalancer_targets_name} --protocol HTTP --port ${target_port} --vpc-id ${vpc_id} )
target_group_arn=$( echo -e "${target_group_response}" | jq '.TargetGroups[] | .TargetGroupArn' | tr -d '"' )
echo "[*] [$( date +'%H:%M:%S')] Create Listener that will forward traffic to registered instances..."
listener_response=$( aws elbv2 --region ${region} create-listener --load-balancer-arn ${alb_arn} --protocol HTTP --port ${listener_port} --default-actions Type=forward,TargetGroupArn=${target_group_arn} )
Crucial for dynamic port forwarding is this “strange” 0 port number mapping in docker-compose.yml:
version: '2'
services:
web:
image: httpd:2.4.32
ports:
- "0:80"
logging:
driver: awslogs
options:
awslogs-group: ecs-medium
awslogs-region: eu-west-2
awslogs-stream-prefix: example
https://www.benedict.cloud/2019/02/10/full-lamp-docker-and-aws-introduction-tutorial/
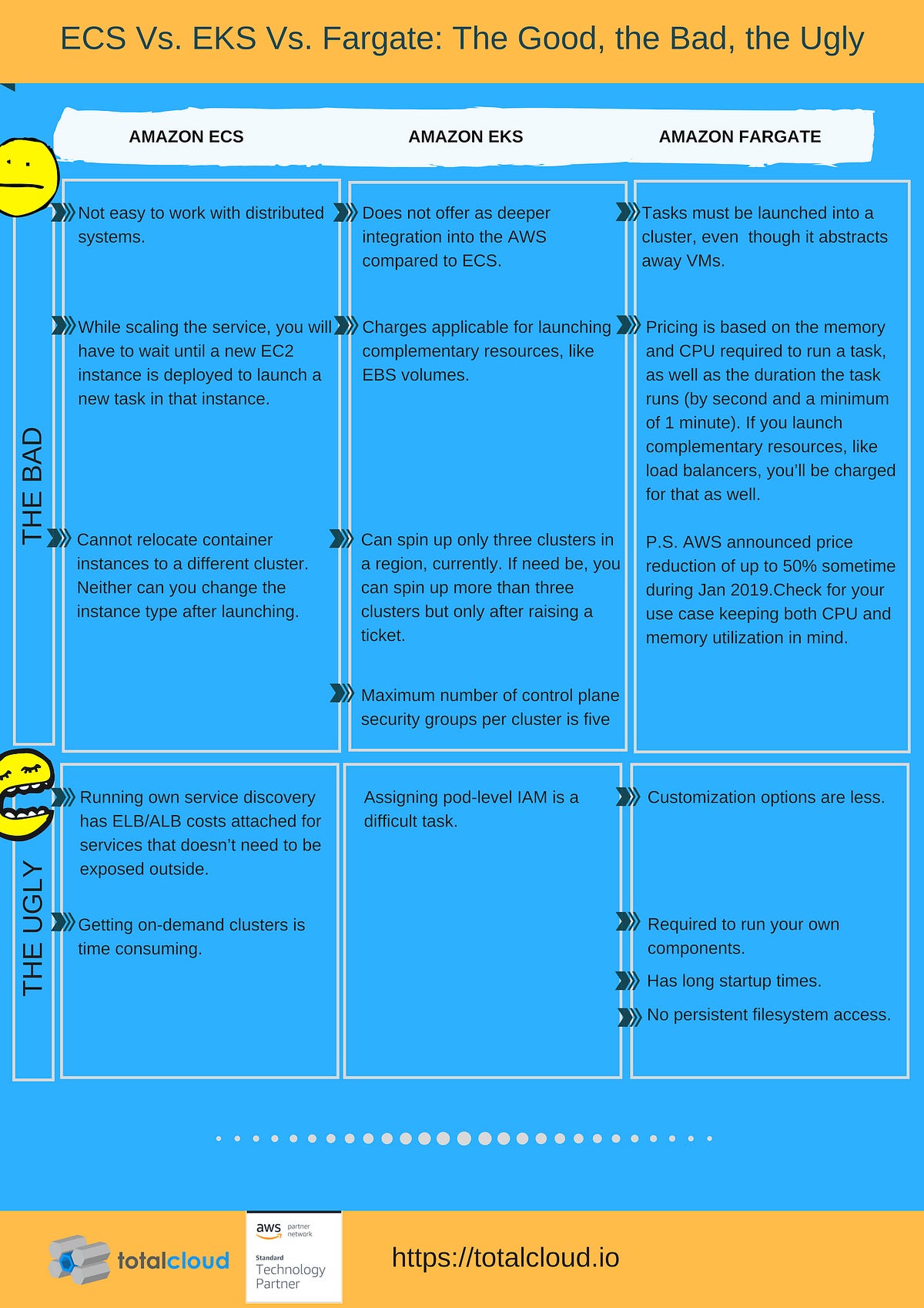
Comparison of AWS Container services:









No comments:
Post a Comment